Antibody dependant mechanisms
Some therapeutic monoclonal antibodies are able to recruit innate immune cells, or complement for destruction of tumour cells. Antineo proposes several assays to decipher such mechanisms both in vitro, ex/in vivo.
Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC)
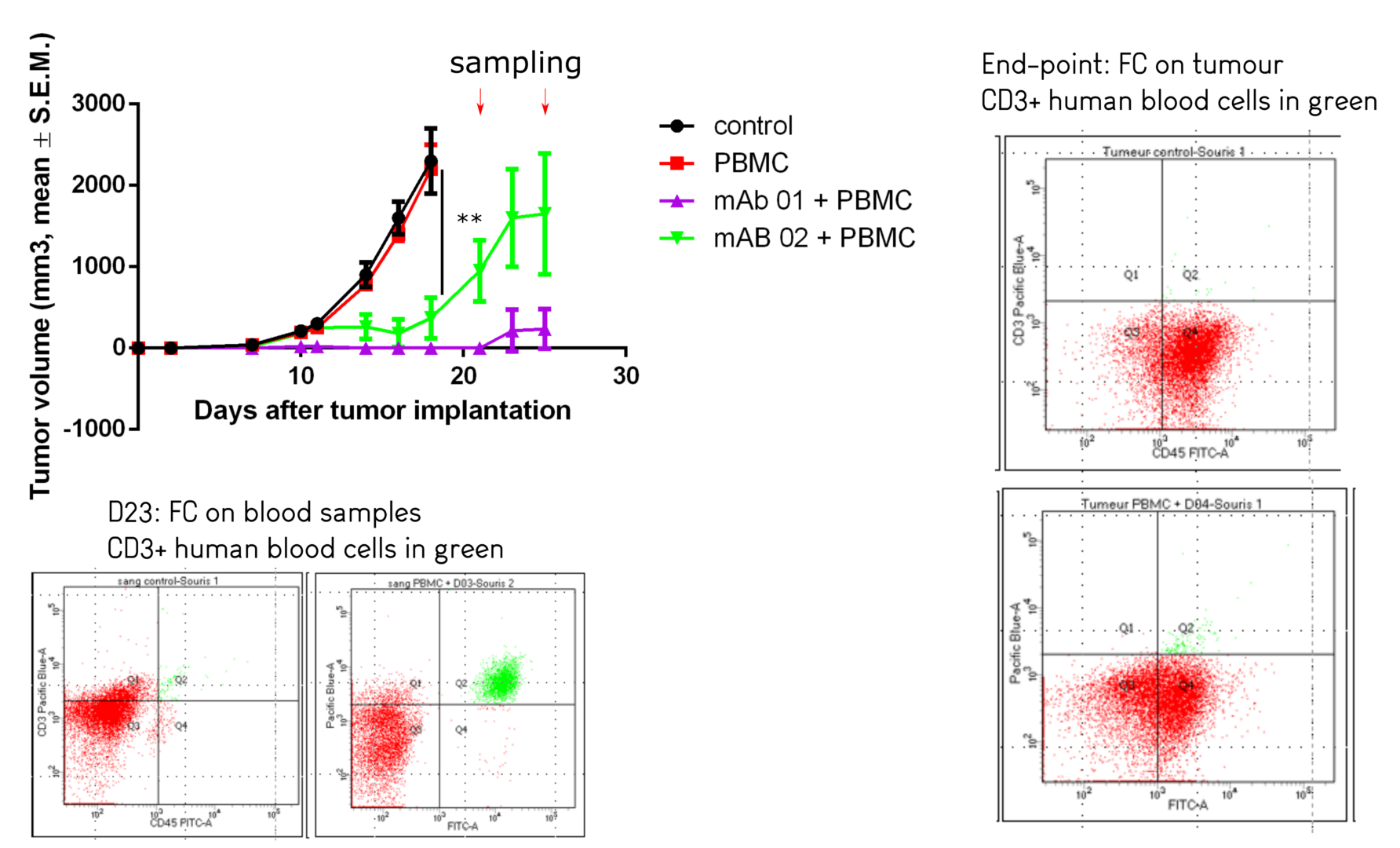
The best described mechanisms involve Antibody Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity in which cells, such as Natural Killer lymphocytes, bind the antibody through their Fcγ receptor and are activated to release cytotoxic products.
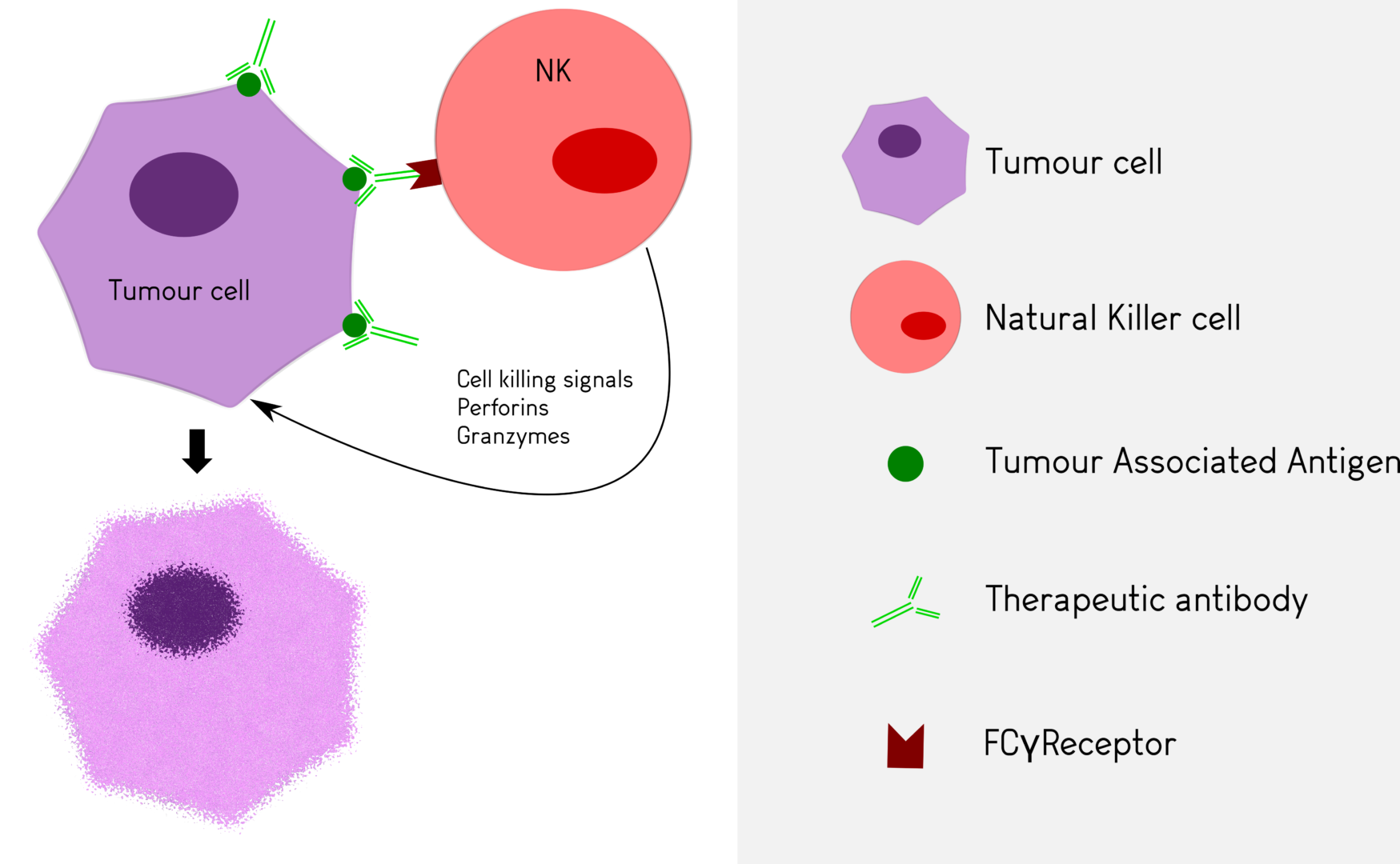
Antibody Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis (ADCP)
In Antibody Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis, phagocytic cells such as granulocytes or macrophages are engaged by the antibody via their Fcγ receptor to destroy tumour cells by phagocytosis.
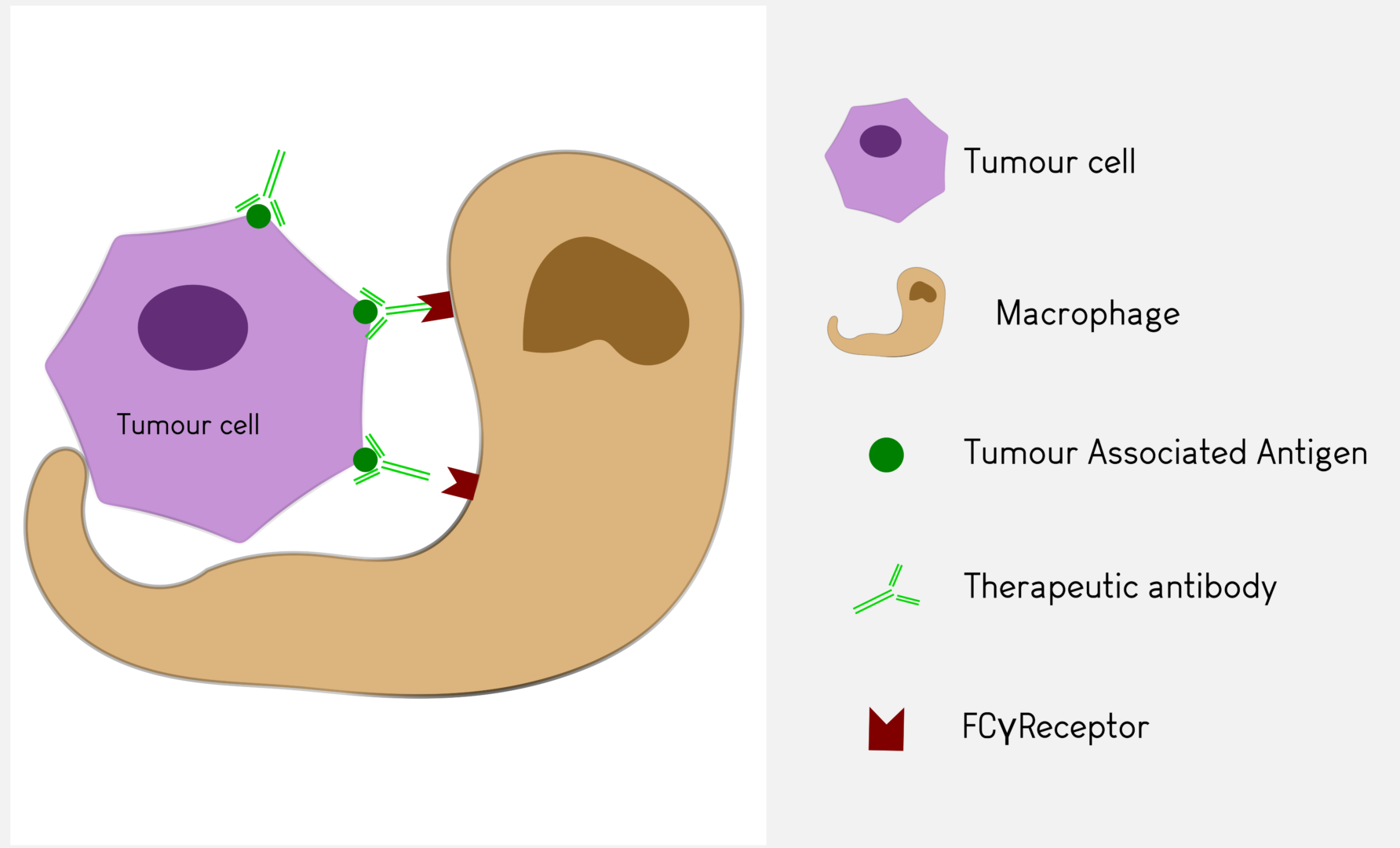
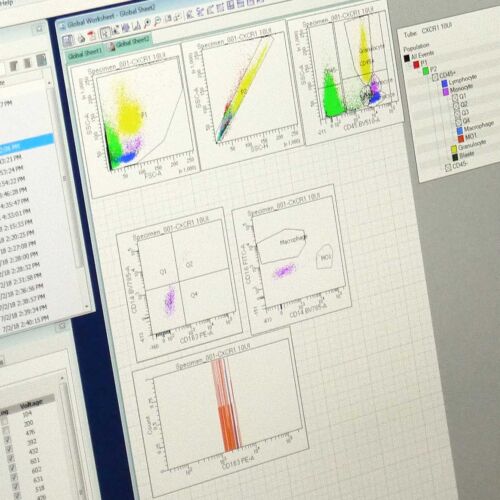
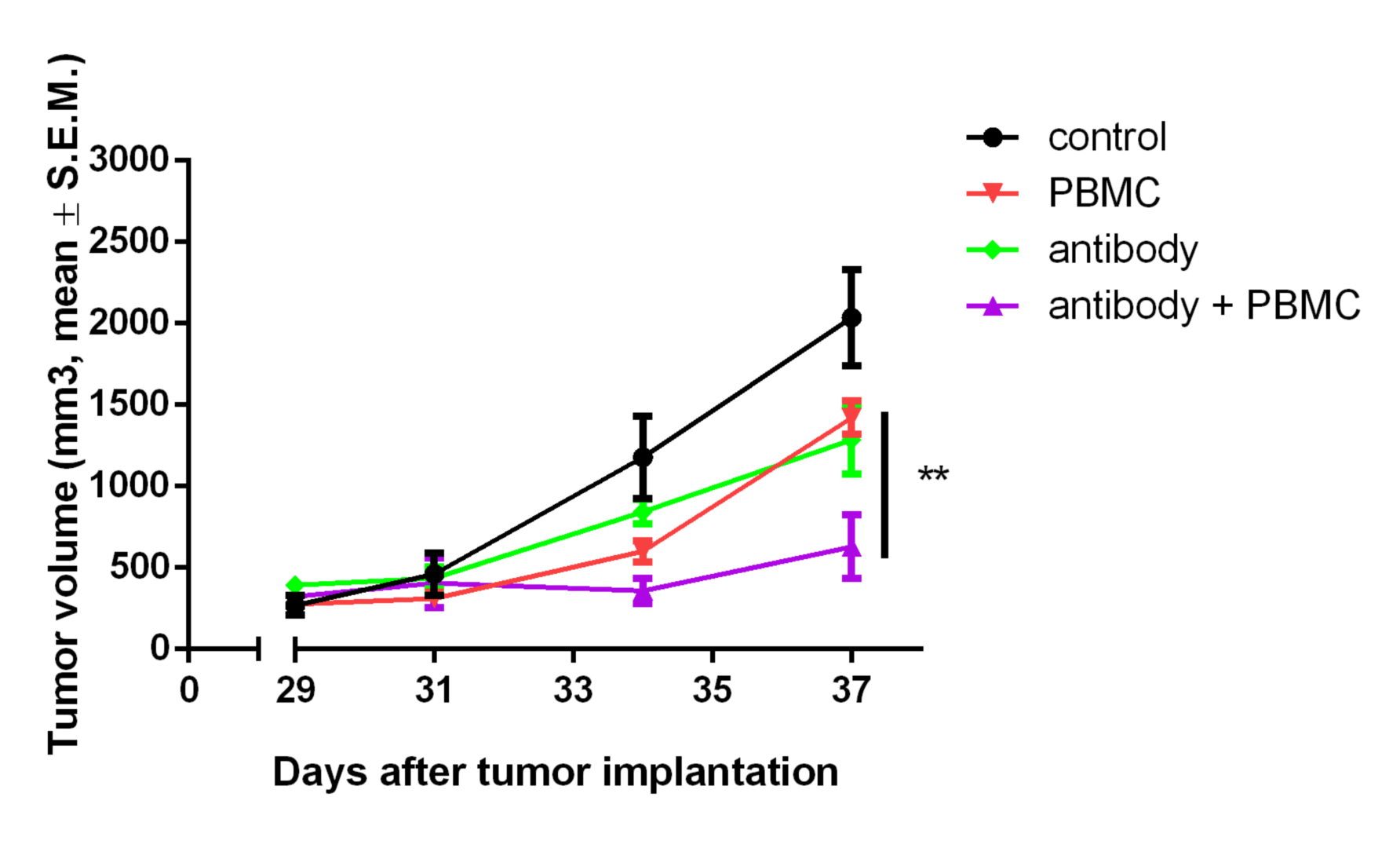
Antineo analyses the ability of your candidate antibodies to perform ADCC and/or ADCP using model cell lines or fresh human effector cells from healthy donors. ADCC is quantified using the release of calcein by tumour cells while ADCP is quantified by flow cytometry, evaluating the transfer of tumour cell fluorescence to effector cells. Both assays can be can be performed with continuous-monitoring, and ADCC can be assessed with our original in vivo assay.
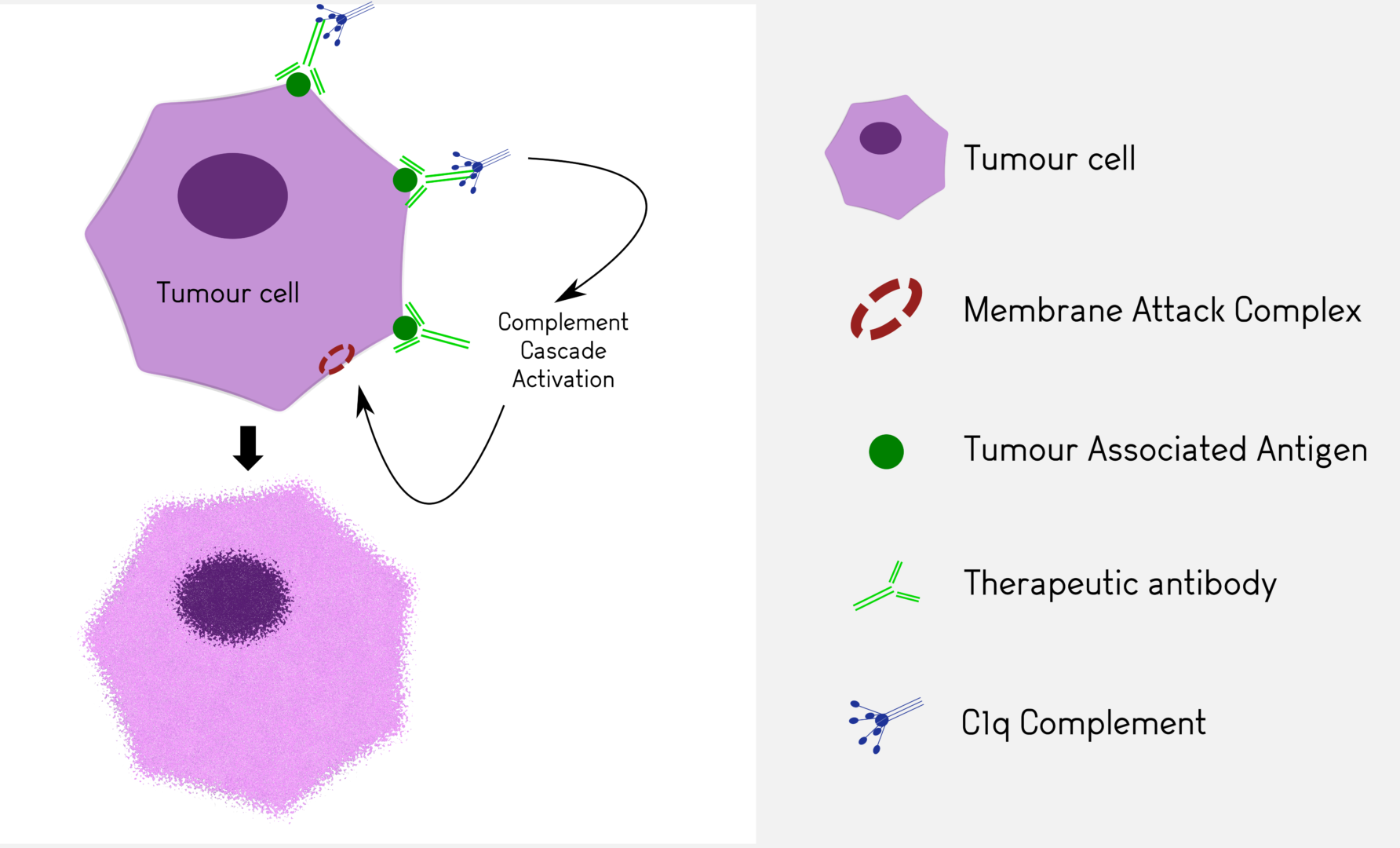
Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC)
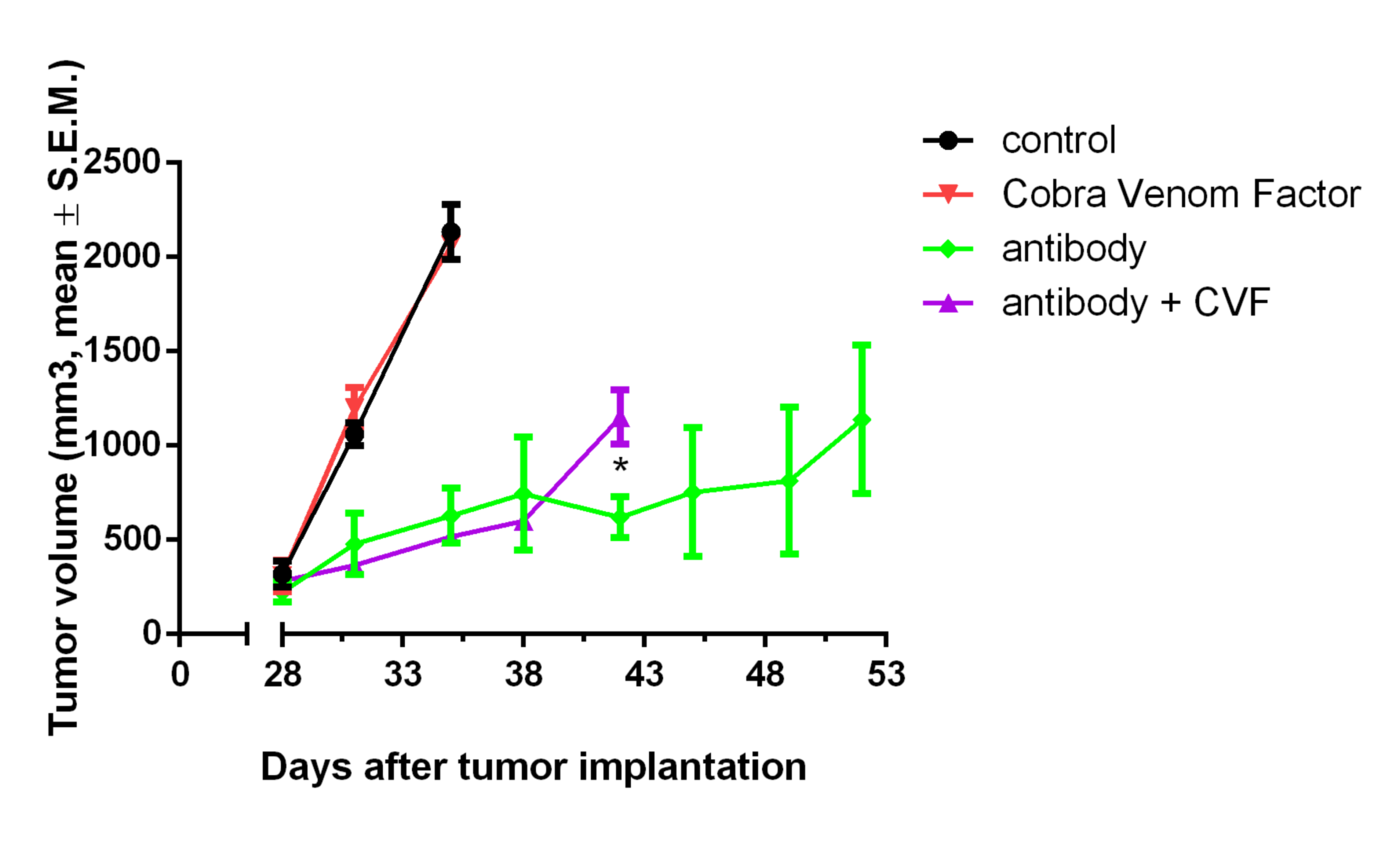
We determine the effect of your antibody on cell lines or fresh human samples in presence of human or rabbit serum containing complement. CDC assays are performed using calcein release. These tests can be completed in vivo using cobra venom as a complement depleting agent (in vivo studies).

 Antineo
Antineo Preclinical services
Preclinical services Tumour models
Tumour models Our Strengths
Our Strengths News & Events
News & Events